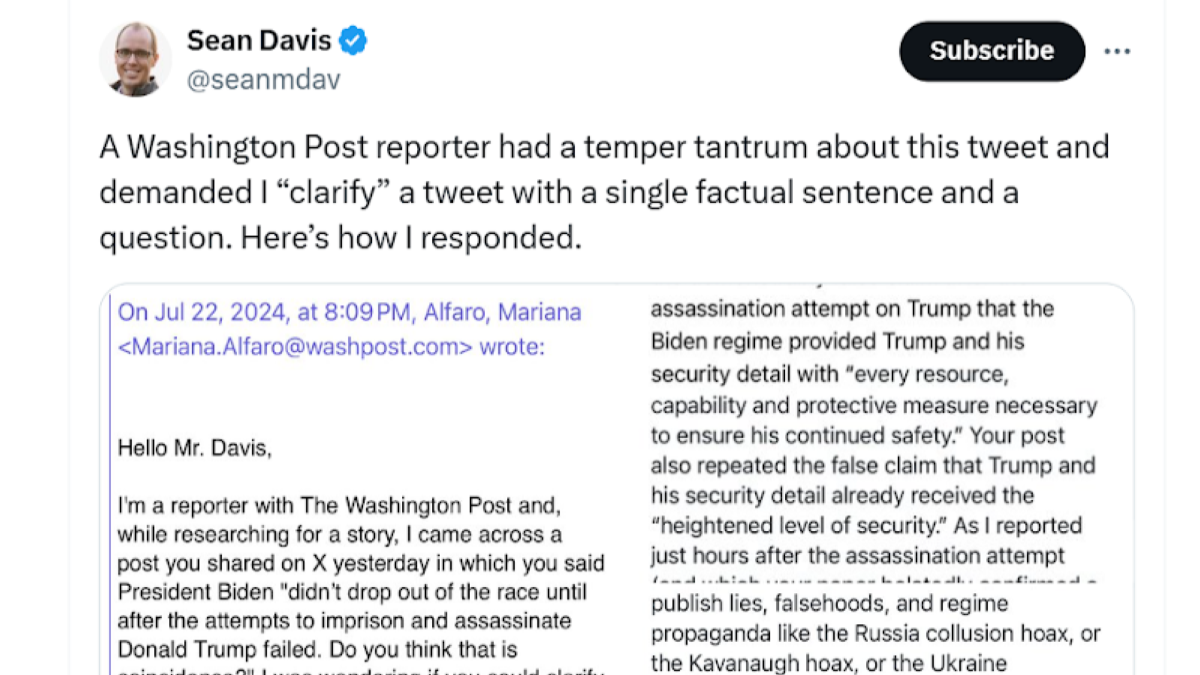
doyouremember.com
Kelly Clarkson Sounds Heavenly Performing Aerosmith Cover
Time and again Kelly Clarkson has proven her music talents are as strong as ever. She continually gets to exercise her melodious pipes thanks to the “Kellyoke” segment of The Kelly Clarkson Show, and a recent performance by Clarkson covering an Aerosmith hit has fans worshipping her divine skills all over again.
42-year-old Clarkson has been hosting her eponymous daytime variety talk show since 2019. Since its autumn premiere, the program has won twenty-two Daytime Emmy Awards, including for Outstanding Talk Show and Outstanding Talk Show Entertainment. Clarkson herself has won Outstanding Entertainment Talk Show Host in 2020, 2021, and 2022. Recently, she reminded fans why her trophy case also includes three Grammy Awards, while tapping into that rugged Aerosmith sound.
Fans are raving after Kelly Clarkson performed a memorable cover of “Angel” by Aerosmith
Kelly Clarkson showed off her heavenly voice in her cover of Angel by Aerosmith / YouTube screenshot
On the July 10 episode of The Kelly Clarkson Show, Clarkson chose “Angel” by Aerosmith for the opening number. Her rendition was particularly emotionally driven, and she emphasized the intense atmosphere with her wardrobe.
RELATED: Steven Tyler Feared One Aerosmith Song Would Ruin His Career
For the occasion, Clarkson donned an all-black jumpsuit and dark shoes. Her shirt of choice flatteringly hugged her figure, while the hem of her pants flared out dramatically. Clarkson completed the look by tying her signature blonde hair back out of her face, showing off subtle but moody makeup. Her jewelry consisted of thick hoops and a delicate necklace.
Vocally, Clarskon had the voice of an angel herself, with fans already praying for more. “I would love for Kelly to make an album of covers,” one viewer suggested, “Her versions are always so amazing!”
Another praised, “That second verse high note, OMG! Right in pitch. So hard to do. Kelly is vocal excellence.”
Continuing the heavenly greatness
Her performance has fans clamoring for a cover album / ImageCollect
Aerosmith released the quintessential power ballad “Angel” in 1988, though it was part of their ‘87 album, Permanent Vacation. “Angel” soared to number 3 on the Billboard Hot 100, at the time quickly becoming their highest-charting single at that time. It is a masterful example of glam metal, with all the grandeur of that movement. Since then, “I Don’t Want to Miss a Thing” outpaced it, becoming the band’s first and only number-one single, but all their charting tracks have been worthy of their place.
MTV TENTH ANNIVERSARY SPECIAL, Aerosmith, from left: Tom Hamilton, Steven Tyler, Bradley Whitford, Joe Perry, Joey Kramer; Michael Kamen, (aired June 16, 1991). ph: George Da Costa / ©ABC / courtesy Everett Collection
It also featured the dream team of lead singer Steven Tyler working in collaboration with Desmond Child. Child has also had a hand in Bon Jovi’s “Livin’ on a Prayer,” “Bad Medicine,” and “You Give Love a Bad Name,” as well as “I Was Made for Lovin’ You” by Kiss, Cher’s “We All Sleep Alone,” and, again with Aerosmith, “What It Takes” and “Dude (Looks Like a Lady),” to just name a few.
Child’s prodigious skill as a songwriter has earned him four Grammy Awards, a Primetime Emmy Award, and induction into the Songwriters Hall of Fame in 2008—and Clarkson’s cover of “Angel” earned itself another few hundred listens back to back to back.
Click for next Article
The post Kelly Clarkson Sounds Heavenly Performing Aerosmith Cover appeared first on DoYouRemember? - The Home of Nostalgia. Author, Dana Daly