
www.theamericanconservative.com
How to Build a Society
Culture
How to Build a Society
Observations from 14 Days in Singapore.
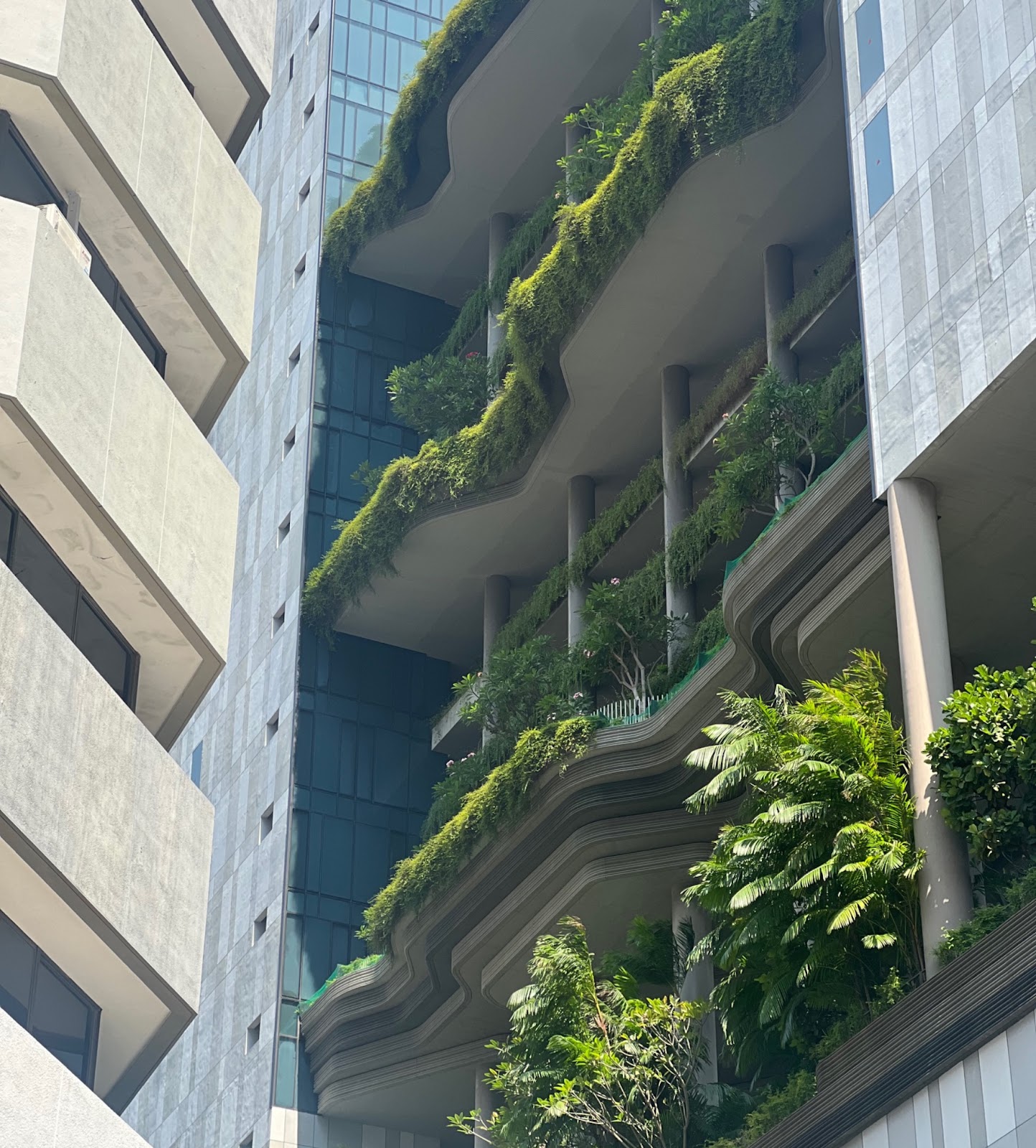
The air is surprisingly clean in Singapore, a futuristic city nestled amid the dense jungle at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula. Chickens roam freely, and monkeys can be spotted along the paths leading downtown, where towering steel skyscrapers stretch toward the sky. Bikes are scattered across the city, left unattended and without locks. There isn’t a single police officer in sight. The atmosphere is sweet and serene; most people dress neatly, seemingly out of a simple, mutual respect for one another. Massive trees rise unexpectedly from the ground. English, Malay, and Arabic street names dot the landscape. Above it all, green canopies—so many green canopies—blend with the gleaming steel architecture that rises above the Singapore Strait.
The lush, vibrant nature of Singapore is no accident. Lee Kuan Yew, the man who crafted the city-state into what it is today, made sure the Southeast Asian nation wouldn’t simply become a concrete jungle for well-heeled capitalists, but a livable, breathable space whose wealth was not only measured by the strength of its currency. “I have always believed that a blighted urban jungle of concrete destroys the human spirit. We need the greenery of nature to lift up our spirits,” Lee wrote in his memoir From Third World to First. “After independence, I searched for some dramatic way to distinguish ourselves from the other Third World countries. I settled for a clean and green Singapore.”
Speaking to Parliament in 1968, Lee, who acted as the city’s first chief gardener, laid out his vision for a green ecosystem within the nation as it rapidly urbanized and industrialized from huts to skyscrapers after Singapore was expelled from Malaysia in 1965. “An elected government cannot have certain sections of the city clean and green and leave the rest to fester,” Lee told lawmakers. As a result of Lee’s efforts, the island nation boasts four nature reserves and more than 300 parks in a space smaller than metropolitan New York.
When Western analysts categorize Singapore, it is usually through the lens of industry and discipline. For as much as Lee enjoyed the natural beauty of his island nation, it was with a cane that he bent its people’s will and shaped Singapore into the business behemoth it is today. Though its people are not immune to the inflationary cycle that has recently stricken the West, their salaries are competitive, their schools are among the most prestigious in the world, and their streets are safer than almost any others. There are BMWs and Benzes and Porsches around every corner, the lap of a luxury that is rare even among the richest of Western societies.
Lee’s dream of a new city for his people and for Asia succeeded, with little thanks to the democratic ideals of the American experiment. Writing in the Washington Post following Lee’s death in March of 2015, Richard Cohen argued that Lee’s legacy said as much about Singapore as it did our downwardly-mobile society stateside. Remarking on the many tributes Lee received from his Western counterparts, Cohen wrote, “We appear to be suffering from an acute case of authoritarian envy.”
Singapore is not an authoritarian society by decree. The People’s Action Party, headed by Lee for more than 50 years, has repeatedly won majorities in election after election, including as recently as 2020, when PAP won 83 of 95 Parliamentary seats.
Lee was determined to steer his nation clear of the mismanagement that has plagued other Asian cities, which have struggled to modernize their infrastructure, from roads to schools, over the last century. The differences, for example, between Singapore and Johor Bahru, a similar-sized Malaysian city on the causeway across the Straits of Johor that connects it to Singapore, are vast and numerous. The citizens of Johor Bahru, living only a bridge away from mainland Singapore, suffer from poor wages, poor literacy, and expensive transport. The threat of violence is present in JB, too, a concern that didn’t cross my mind once during the two weeks I spent crisscrossing Singapore in early February.
From the moment I exit the plane at Changi Airport, one of the largest transportation hubs in all of Asia, Singapore and its people aim to impress. Named the best airport in the world on 12 different occasions by Skytrax, Changi is a microcosm of everything I will experience in Singapore over the next 14 days. Besides the airport’s luxurious shopping malls, its healthy grocery stores, and air-conditioned rainforest, the hurly-burly of air travel itself is reduced to a mere exchange of pleasantries. I breeze through biometric security checks and into the nation within 15 minutes of landing.
At no point will the stark contrast between Asia’s first-world infrastructure and my American perception of it be more apparent than at this airport. Sleek, streamlined technology efficiently moves hundreds of thousands of passengers through the concourse each day in a seamless experience. Leaving Dulles, on the other hand, was a chaotic mess; the return was even worse. Uninterested, overwhelmed boomers sluggishly checked passports at Immigration Services, while tetchy TSA agents used what felt like outdated scanning devices between bites of greasy fast food.
In Singapore, everything runs like clockwork. The subways and roads are pristine, and the people are dressed for success. In the mornings, men and women of all ages are out jogging and stretching. By evening, markets are buzzing with food and young professionals; then many of them are back to jogging. It’s a culture defined by relentless, unwavering productivity. In all of Southeast Asia, Singapore stands out like a vibrant rose in a garden of withered flowers.
The women wear their hair in beautifully woven buns, and everyone sports Bluetooth headphones. The Blue Line MRT, heading toward Suntec City in the heart of the Downtown Core, is so packed that it’s hard to breathe. Surrounded by busy professionals and foreigners, I can’t help but long for my spacious, open home on the American plains.
The vestiges of the British Empire are unmistakable in the downtown area: the gothic St. Andrews Cathedral, the Norman Foster–designed Supreme Court, the palatial Raffles Hotel, which once hosted the likes of Rudyard Kipling and Joseph Conrad. Though Singapore concretely feels like a city of the new, it has retained the masterpiece watermarks of the old within the fortress of big business.
Singapore dominated the top end of the inaugural Fortune Southeast Asia 500, released in 2024. Eighty-five companies from the island nation, in sectors as diverse as banking, commodities, oil, and infrastructure, were featured on the list. Half of its wealthiest 10 companies are based in Singapore. This, as much as the thickets of lush greenery and the well-behaved and well-housed populace, is the legacy of Lee, who maneuvered his tiny nation into one of the most competitive capitalist societies in the whole world.
Lee’s project of rapid Westernization made his city-state a marvel of the Orient—so much so that following the departure of Chairman Mao Zedong and Deng Xiaoping, Chinese Communist Party officials embraced elements of Lee’s capitalist vision and the two nations came to an earnest and mutual respect. Lee visited Beijing many times during his stewardship; when he died in 2015, the Chinese foreign ministry released a statement that championed Lee as “a uniquely influential statesman in Asia and a strategist embodying oriental values and international vision.”
True to those words, it’s impossible to overlook the internationalist scope of Singaporean culture during my two-week jaunt on the Other Side of the World. Buddhists, Muslims, Christians, Taoists, and Hindus live in blended harmony in this place. Mere blocks from St. Andrew’s Cathedral beats the heart of the Muslim community—Haji Lane and its ornate Sultan Mosque in the district of Kampong Glam. The striking religious landmark, built in 1826, is one of 72 mosques in the region. More than half a million residents who call Singapore home identify as Muslim.
Buddhism is the largest religious demographic in the nation, with more than one out of every 3 Singaporeans identifying themselves as such, although the sight of monks in orange robes is less common here than in neighboring countries such as Thailand and Laos. Catholics and other Christians account for about 20 percent of the Singaporean population, due in equal parts to British colonialism and Lee’s promotion of the adoption of English as a primary language for all of Singapore’s citizens to learn. The prominence of English, from its presence on signs and atop infrastructure to the locals who speak it well without hesitation, makes visiting or living in Singapore relatively easy in comparison to other Southeast Asian countries.
Though Lee recognized the important role English played in westernizing Singapore, in 1966 he mandated that all citizens learn their “mother tongue,” a language associated with their own unique cultural heritage. Lee created the Prime Minister’s Book Prize, which pushed students to learn the language of the West while retaining rich linguistic traditions of the Orient.
“If we were monolingual in our mother tongues, we would not make a living,” Lee later reflected in his memoir. “Becoming monolingual in English would have been a setback. We would have lost our cultural identity, that quiet confidence about ourselves and our place in the world.”
On one of my first nights in the city, my sister and her husband take me to a hawker center; an open-air, cafeteria-style zone with nearly a hundred different, cart-sized eateries. Wontons, prata, satay, popiah, fish soup—all of Asia’s most delectable desires are on display at fair prices. I must have gained five pounds at the Little India hawker center alone. These centers are a dizzying delight for foodies.
As with all of Singapore, there are strict rules that are enforced here, not by policemen with batons, but by the heavy expectations of a high-trust society. Although a few day staff man the trash bins at the hawker centers, patrons are expected to clean their own tables and bus their plates. Not to do so is a matter of shame and, to my American astonishment, I don’t see a single scrap of food or misplaced dish on the tables in any of the more than 15 hawker centers I dine at during my stay.
But it’s not just respect for one another that keeps the citizens of Singapore on their best behavior. It’s also the threat of real, actual punishment. In eulogies of Lee, the Singaporean’s preference for the cane is often cited as part of his paternalistic stewardship. When American teenager Michael Fay, a student at the Singapore American School, was found guilty of vandalism in 1994, he was flogged four times despite appeals.
“Can we govern if we let him off and not cane him?” Lee responded when the punishment was questioned abroad. “We’ll have to close shop. That’s my view. I am an old-style Singaporean who believes that to govern you must have a certain moral authority. If we do not cane him because he is an American, I believe we’ll lose our moral authority and our right to govern.”
Though intellectuals often view Lee’s form of punishment as archaic and out of step with the modernization efforts of the city-state, a Los Angeles Times poll conducted at the time of the caning revealed that 49 percent of Americans supported the punishment, despite protests from then-President Bill Clinton. Additionally, 36 percent of respondents expressed support for introducing similar caning measures in the U.S. for teen vandals.
One of Lee’s most famous quotes—“Whoever governs Singapore must have that iron in him, or give it up”—encapsulates his determination to govern as necessary, regardless of Western liberal values. He famously stated: “This is not a game of cards! This is your life and mine! I’ve spent a whole lifetime building this, and as long as I’m in charge, nobody is going to knock it down.”
Fay’s caning served not only as a lesson in Singapore’s resilience to international protests, but also as a message to its people—that their commitment to the national project would not be undermined by the double standards of liberal critics abroad. Since independence, Singapore has been an all-or-nothing endeavor, with Lee and his people fully invested in its success. This mindset helps explain the ubiquitous surveillance in the city-state: There are over 100,000 CCTV cameras, or 18 per 1,000 people, making it the third-most surveilled city in the world. (Besides Singapore, Chinese cities dominate the list.)
In Singapore, the feeling that you are being watched is ever-present, from the moment you enter the country at Changi Airport to the time of your departure. In grocery stores, on the subways, outside restaurants, and in hotel lobbies, there is always a camera judging your movements and actions. Depending on your vantage point, Singapore is the modern expression of a dystopian security state. Especially from a Western perspective, immediate concerns about privacy and freedom arise in response to such extensive monitoring. The very ethos of America and our people is a natural desire to be free of state surveillance, and many of our greatest slogans and people have embodied that streak of independence.
Proponents of the “watched city” concept argue that heavy surveillance, combined with strict punishments for drug traffickers and violent offenders, has contributed to the creation of a “perfect society.” I can’t deny that during my time in Singapore, I felt safer than I’ve ever felt in any major city. I’ve been to Rome, Lisbon, Paris, Dublin, Bangkok, New York City, Los Angeles, Tucson, Dallas, and Detroit, and I can tell you firsthand that each of these cities has areas marked by blight and criminal activity that even the most seasoned travelers need to navigate carefully. But not Singapore.
A big part of this safety is due to the city-state’s zero tolerance for theft, harassment, drug use, and violence. Strict punishments play a significant role in deterring criminal behavior. For example, an Indian national who stole less than $1,000 worth of perfume at Changi Airport this year is now facing up to seven years in prison. And yes, they still hang people in Singapore. Since resuming the death penalty after a brief hiatus during the Covid pandemic, Singapore has executed 25 people—most for drug trafficking—despite condemnation from international critics.
Yet the threat of punishment alone isn’t what earns Singapore its reputation as the “safest city in the world.” The social cohesion fostered by Lee Kuan Yew’s vision of a genuinely integrated society, built on values of productivity, ingenuity, and fairness, has contributed to a nation where poverty is low, schools are world-class, healthcare is accessible, unemployment is minimal, and the standard of living is among the highest globally.
Another key factor that keeps the streets of Singapore free from petty criminals and homeless vagrants is its planned housing, a central theme to Lee’s vision for the country. More than half of the 6 million people who call Singapore home live in high-rise apartments built by the government that defy American preconceptions of what government-built housing looks like. Through subsidized housing, Lee provided homes for nearly 75 percent of the population who previously lived in tin-walled huts.
The apartments, known as HDB flats, come with a 99-year lease and the knowledge that someday the properties will be returned to the Singaporean government, which built more than 50,000 of them during an expansion period beginning in the late 1940s. The average flat is about 750 square feet with three bedrooms in a condo-like setting. On the ground floor is often a large, open-air deck where residents can mingle and children can play. In 1964, Lee introduced his Home Ownership for the People Scheme, which sought to house every single Singaporean in a bid to shore up potential tensions in a country of immigrants.
“My primary preoccupation was to give every citizen a stake in the country and its future,” reads a placard in Lee’s writing at a hawker center near Farrer Park in the Kallang residential zone. “I wanted a home-owning society.”
Blending a deeply different nation of immigrants took more than providing subsidized housing for all—it took making them live together. In 1989, the Singaporean government mandated racial quotas that required Malays, Chinese, and Indians to live among each other in the same residential zones, essentially outlawing the formation of racial districts.
Speaking of the decision in 2015, President Tharman Shanmugaratnam argued that “the natural workings of society” would have led to “mistrust, discomfort, bigotry and what we see in abundance in many countries in the world today.”
“Once people live together, they are not just walking the corridors together everyday, taking the same elevator up and down,” Shanmugaratnam said. “Their kids go to the same kindergarten, their kids go to the same primary school. The most intrusive social policy in Singapore has turned out to be the most important.”
Walking through the streets of Singapore, it is clear that the project has been a success. Christian symbols are visible everywhere, as Muslim men stream into the mosques for morning prayers. Just a metro stop away in Little India, hundreds of Hindu devotees gather at the Sri Veeramakaliamman Temple on a Wednesday afternoon. Throughout my stay, I never once feel tension rising between the city’s diverse communities. This multicultural harmony is not merely a stroke of luck, but a conscious effort rooted in the pursuit of peace, embodied in Singapore’s National Pledge: “We, the citizens of Singapore, pledge ourselves as one united people, regardless of race, language or religion, to build a democratic society based on justice and equality so as to achieve happiness, prosperity and progress for our nation.” The words are often recited by Singaporeans at public events and in schools.
On my final day in the Orient, I catch the blue line train to the downtown area. A staff member stands on the platform holding a sign that reads, “No eating/drinking in train or station.” Whether it’s the cameras, the threat of punishment, or simply mutual respect, I never witness a single crumb of food or bottle of liquid on any of the hundreds of trains I take during my stay.
People stand shoulder to shoulder, quietly. There are no boomboxes blaring, no teenagers performing acrobatics for spare change as you might see in the rundown cars of the Bronx or Columbia Heights. No one is speaking loudly on the phone. There are no angry stares, no strange smells, and no frantic individuals shouting in the corners of the car. There are clear expectations here, and the people rise to meet them. It’s certainly not easy. I can see that. It takes a specific kind of person, committed to a particular way of life, to make it work. But when it does, it truly works. The trade-offs—limited privacy and restricted freedoms—have contributed to the creation of a society unlike any other in the world. At its worst, Singapore represents something that America often struggles to achieve: a society that is safe, clean, quiet, and undeniably boring.
“Boring” is the last word I’d use to describe my homeland. The big, creative, rambunctious energy of the West and especially America cannot be overlooked here among the quiet streets and tempered people. I miss our Red, White, and Blue every moment I am away, warts and all. America has a pace and intensity that is unmirrored the world over which makes its blights all the more worth suffering. As I consider what makes a great society, what elevates a people—their great dreams and collective aspirations—I can’t help but marvel at our own chaotic blend.
When I arrive in downtown Singapore, young people are relaxing on palatial garden bluffs. Everyone here wears shoes—not Birkenstocks, huaraches, or sandals, but leather derbies, brown oxfords, and black Park Avenues. In their footwear lies a revealing truth about Singaporeans: They’re all business. There’s a refined elegance at work here, one that extends even to the luminous quality of the nation’s impeccably designed banknotes.
The undeniable success of Singapore, from the general health and wealth of its people, to its stature as a hotbed for finance and tech in the 21st century, cannot be overstated. In less than half a century, Lee transformed a third-world slum into a thriving business paradise admired around the globe. While the United States and its Western allies struggle with the cultural and economic stagnation of the 21st century, new models of governance, inspired by Singapore’s bold and unforgiving approach, may be necessary to forge a path forward. Lee understood that the road ahead wouldn’t be easy, and that both the sacrifices of the people and his own leadership would not always be celebrated. Yet he pressed on. How do you build a society? With an iron fist.
Speaking from his deathbed in 2015, Lee summarized a life’s work: “At the end of the day, what have I got? A successful Singapore. What have I given up? My life.”
The post How to Build a Society appeared first on The American Conservative.















 Rumble
Rumble
